What Type Of Government Is The US? Unpacking America's Unique System
Have you ever wondered about the true nature of the United States' political setup? It's a question many folks ask, especially when news headlines talk about different parts of the government doing their work. Getting a clear idea of how the US is governed really helps make sense of how decisions get made and who holds the say. This understanding, you know, is pretty important for anyone living here or just interested in how big countries manage themselves.
You see, when people talk about the US government, they often use a few different words, and that can make things a little fuzzy. Is it a democracy? A republic? Something else entirely? It’s a good question to ponder, and the answer is actually a bit more layered than just one simple label. We’ll look at what makes it tick, piece by piece, so you can have a really solid grasp of the whole picture.
So, we're going to take a friendly stroll through the key ideas behind America's way of running things. We'll explore the parts that make it special, how power is shared, and what those big words like "federal" and "constitutional" really mean for everyday life. It's about getting a practical feel for how the country operates, and that, in a way, is what we're here to figure out together.
Table of Contents
- What's the Official Label?
- Federal: How Power Gets Split Up
- Constitutional: The Big Rule Book
- Republic: When Representation Matters
- The Three Big Branches of Government
- Checks and Balances: Keeping Things Fair
- FAQ: Your Questions Answered
- Bringing It All Together
What's the Official Label?
When you ask what kind of government the United States has, the most precise answer, you know, is that it’s a federal constitutional republic. That's quite a mouthful, isn't it? But each of those words tells us something really important about how the country is run. It’s not just one thing, but a mix of a few big ideas that work together. This combination makes it pretty unique in the world, actually.
This particular setup means a few things right off the bat. It tells us that power isn't all in one place, that there's a foundational document guiding everything, and that people get to pick representatives to speak for them. It’s a system that, in some respects, has grown and changed over a long time, but these core principles have stayed put. So, let’s break down each part of that label to really get a handle on it.
Federal: How Power Gets Split Up
The "federal" part means that power is shared between a central government and smaller, local governments, like the states. It's not just one big government telling everyone what to do, which is kind of a big deal. Instead, the national government handles certain things that affect the whole country, while state governments manage matters closer to home. This division, you know, is a core idea.
For example, the federal government might take care of national defense, printing money, or dealing with other countries. But then, state governments handle things like schools, local roads, and many day-to-day laws that affect people directly. This way of sharing power, it's almost like a team effort, ensures that decisions can be made at the right level, often closer to the people they affect. It’s a balance, really, to make sure both big and small issues get attention.
This system, you know, helps keep any single part of the government from getting too much authority. It's a way to spread out the responsibilities and make sure different areas have a say in how things operate. This setup, in a way, was quite revolutionary when it was first put into place, and it still shapes how things work today. It's a defining feature of the US government system, and one that people often talk about when discussing states' rights versus federal authority.
Constitutional: The Big Rule Book
When we say "constitutional," it means there's a written set of rules that everyone, including the government itself, has to follow. This document, the US Constitution, is like the supreme law of the land. It lays out how the government is supposed to work, what powers it has, and, very importantly, what rights the people have. It’s a foundational piece of paper, and people often refer to it when there are questions about what's allowed and what's not.
This Constitution, you know, sets limits on what the government can do. It's there to protect individual freedoms and prevent any one person or group from becoming too powerful. It also outlines the structure of the government, creating different branches and defining their jobs. So, it's not just a list of ideas; it's a practical guide for how the entire system should operate, really.
It's interesting, too, that this document can be changed, but it’s a very difficult process. This means it's meant to be stable and long-lasting, but also able to adapt over time if needed. The fact that it’s a written constitution provides a clear reference point for everyone, from citizens to lawmakers, about the basic principles of the country. This provides a sense of order and predictability, which is quite important for a stable society.
Republic: When Representation Matters
The "republic" part of the label means that the people choose representatives to make decisions on their behalf. Instead of everyone voting on every single issue, which would be pretty chaotic in a big country, we elect people to go to Washington D.C. or our state capitals and speak for us. This way, you know, our voices are still heard, but the actual day-to-day work of governing can get done more efficiently.
This is different from a "pure democracy," where every single citizen would vote directly on every law or policy. While the US does have elements of direct democracy, like referendums in some states, the overall system is set up for representative governance. So, we pick our leaders, and they, in turn, make the choices that shape our lives. It's a practical way to manage a large and diverse population, you know, giving everyone a say through their chosen spokespeople.
The idea here is that these representatives are supposed to listen to the people who elected them and act in their best interests. It's a system that relies on trust and accountability. If people aren't happy with their representatives, they have the chance to choose different ones in the next election. This gives citizens a powerful tool to shape their government, and that, in a way, is a core part of what a republic means.
The Three Big Branches of Government
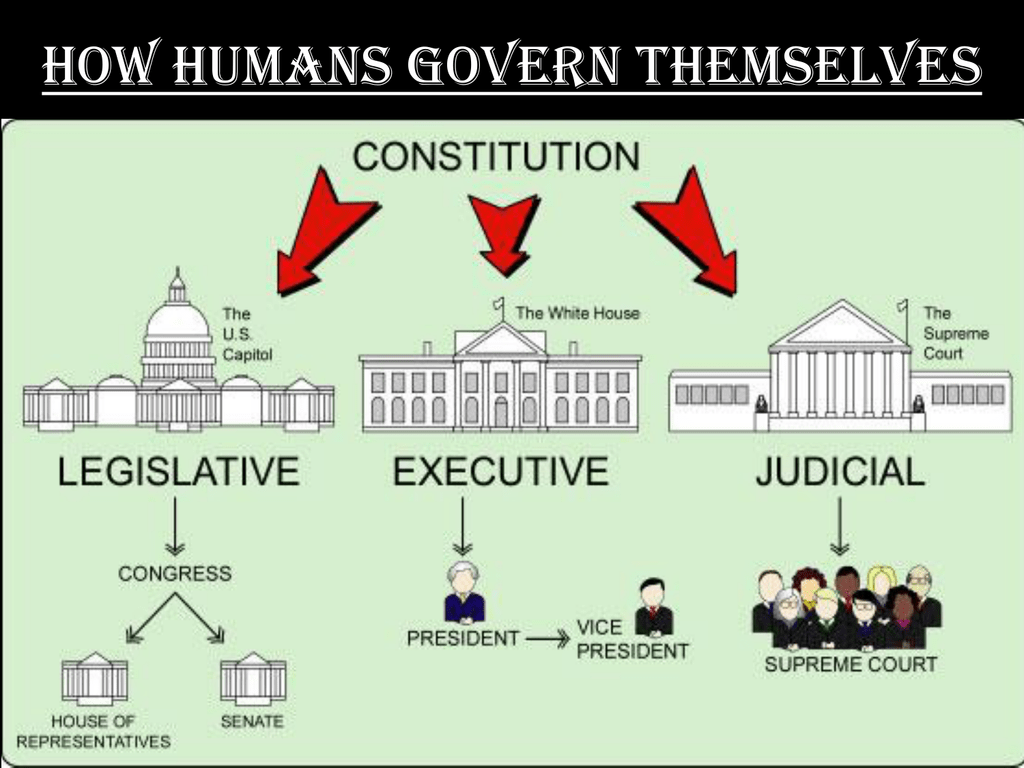
The US government, as laid out in the Constitution, is divided into three main parts, or branches. This division is a really clever way to keep power from getting too concentrated in any one place. Each branch has its own specific jobs and responsibilities, and they are designed to work both independently and together. It’s a system meant to balance things out, you know, and prevent any one group from having total control.
This idea of separate branches, often called the "separation of powers," is a fundamental principle of the US system. It makes sure that different groups of people are involved in making, carrying out, and interpreting the laws. As the text mentions, from the very origins of the American state, this structure was seen as key to a fair and lasting government. It's a design that has been studied by many other countries, too.
The Legislative Branch: Making Laws
This branch is responsible for creating laws, and it's made up of the Congress. Congress has two parts: the Senate and the House of Representatives. People in both the Senate and the House are elected by citizens from their states or districts. So, in a way, this is where the people's voices, through their representatives, really come together to shape national policy.
The Senate has two members from each state, regardless of how many people live there. This gives smaller states an equal say. The House of Representatives, on the other hand, has members based on each state's population, meaning states with more people get more representatives. This dual structure ensures both equality among states and representation based on population size, which is quite a thoughtful design, really.
Their main job, of course, is to write and pass laws. But they also have other important duties, like declaring war, approving treaties with other countries, and controlling government spending. They also have a say in confirming presidential appointments, which is a big check on the executive branch. This branch, you know, is where a lot of the public debate about new rules happens.
The Executive Branch: Carrying Out Laws
The executive branch is headed by the President of the United States. This is the part of the government that carries out the laws that Congress makes. The President is also the Commander-in-Chief of the armed forces, which is a huge responsibility. So, they don't just sign bills; they lead the entire federal government in its day-to-day operations, which is quite a task, really.
The President also has a team of advisors, called the Cabinet, and various departments and agencies that help manage everything from national parks to foreign relations. This branch is about putting policies into action and making sure the country runs smoothly. It’s a very visible part of the government, and the President, you know, often becomes the face of the nation.
Interestingly, the text mentions that the President combines the role of a monarch as head of state with a prime minister's role. This means the President serves as both the ceremonial leader of the country and the active head of the government. This dual role, you know, gives the President a unique position in the world, representing the nation while also being directly involved in its daily governance.
The Judicial Branch: Interpreting Laws
The judicial branch is made up of the court system, with the Supreme Court at the very top. Their main job is to interpret the laws and make sure they are applied fairly. If there's a disagreement about what a law means, or if a law goes against the Constitution, the courts step in to make a ruling. This is a very important role, you know, because it ensures that laws are understood and applied consistently across the country.
The Supreme Court, in particular, has the power of "judicial review," which means it can declare a law passed by Congress or an action taken by the President to be unconstitutional. This is a powerful check on the other two branches, making sure they stay within the bounds set by the Constitution. So, in a way, the courts are the ultimate guardians of the rule book, ensuring its principles are upheld.
Judges in the federal system are appointed, not elected, and they serve until they retire, resign, or are removed through a special process. This is meant to keep them independent from political pressures, allowing them to make decisions based purely on the law, not on popular opinion. This independence, you know, is seen as vital for a fair and impartial justice system, which is pretty essential for any stable society.
Checks and Balances: Keeping Things Fair
Beyond just separating the powers, the US system also has something called "checks and balances." This means that each branch has some ability to limit the powers of the other two branches. It's like a built-in safeguard to prevent any one part of the government from becoming too strong. This system, you know, is designed to encourage cooperation but also to create friction when necessary to protect the system itself.
For example, Congress can pass a law, but the President can veto it. Then, Congress can override that veto with enough votes. The President appoints judges, but the Senate has to approve those appointments. The courts can declare laws unconstitutional, as we just talked about. These interactions, you know, are constant and make sure no single branch can just do whatever it wants. It's a very dynamic system, actually.
This intricate web of shared and limited powers ensures that different perspectives are considered before major decisions are made. It's a system that, in some respects, forces compromise and deliberation, which can be slow sometimes, but it’s also meant to be very stable. The framers of the Constitution, as Britannica points out, really thought about how to prevent tyranny and protect liberties through this very design. It's a pretty smart way to keep things balanced, honestly.
FAQ: Your Questions Answered
Here are some common questions people often ask about the US government system, you know, to help clear up any lingering confusion.
What form of government does the United States have?
The United States operates as a federal constitutional republic. This means power is shared between national and state governments, a written constitution guides everything, and citizens elect representatives to make decisions for them. It's a pretty specific blend, you know, that has evolved over centuries.
Is the US a democracy or a republic?
This is a common question, and the answer is a bit of both, but primarily a republic. While it has democratic elements where people vote, the core idea is that citizens elect representatives to govern. So, it's a representative democracy, which is, in essence, a republic. It's not a direct democracy where everyone votes on every issue, that's for sure.
How is power divided in the US government?
Power is divided in two main ways: federally and by branches. Federally, power is split between the national government and state governments. Within the national government, power is divided among three separate branches: the legislative (Congress), executive (President), and judicial (courts). This system, you know, is designed to prevent any one part from becoming too strong.
Bringing It All Together
So, when we ask, "What type of government is the US?", the answer points to a really thoughtful and layered system. It’s a federal constitutional republic, a blend that ensures power is shared, rules are clear, and people have a voice through their chosen representatives. This setup, you know, with its distinct branches and clever checks and balances, aims to keep things fair and balanced for everyone. It's a system built on ideas that have stood the test of time, adapting as the country grows and changes, even today.
Understanding these different parts helps us make sense of how decisions get made and how the country operates. It shows us why different parts of the government sometimes seem to be at odds, but also how they're meant to work together for the common good. To learn more about how governments around the world work, you could check out Britannica's overview of government forms, which is a pretty good resource. This whole system, in a way, is designed to be resilient and to represent a wide range of people and ideas.
And if you're ever curious about other foundational skills that help us engage with information, like getting faster at typing to express your thoughts, you can always Learn more about typing on our site. Or, you know, if you want to test your current skills, you could link to this page . It’s all about understanding the tools and systems that shape our lives, whether it's how a country is run or how we communicate. This knowledge, you know, is really valuable for anyone wanting to be an active part of the world around them.

What Type of Government Does the US Have?

Type of Government. 350254 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Type Of Government